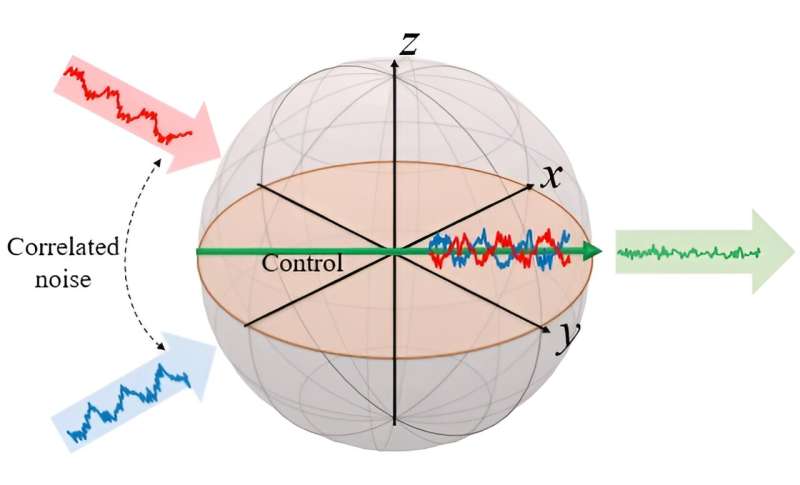
Bloch sphere qubit exposed to cross-correlated noise (blue and red). The method destructively cancels this noise, resulting in excellent performance. Credit: Physical Review Letters (2024). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.132.223601
Researchers have developed a new method to significantly increase the performance of quantum technology by using the cross-correlation of two noise sources to extend the coherence time, improve control fidelity and increase sensitivity for high-frequency sensing. This innovative strategy addresses key challenges in quantum systems, offers a tenfold increase in stability, and paves the way for more reliable and versatile quantum devices.
The work is published in a journal Physical inspection letters.
Researchers have made a major breakthrough in quantum technology by developing a new method that dramatically improves the stability and performance of quantum systems. This ground-breaking work addresses the long-standing problems of decoherence and imperfect control, paving the way for more reliable and sensitive quantum devices.
Quantum technologies, including quantum computers and sensors, have enormous potential to revolutionize fields as diverse as computing, cryptography, and medical imaging. However, their development has been hampered by the harmful effects of noise, which can disrupt quantum states and lead to errors.
Many traditional approaches to noise mitigation in quantum systems primarily focus on temporal autocorrelation, which examines how the noise behaves over time. Although effective to some extent, these methods fall short when other types of noise correlations are present.
The research was conducted by experts in quantum physics, including Ph.D. student Alon Salhov under the guidance of Prof. Alex Retzker of the Hebrew University, Ph.D. student Qingyun Cao under the guidance of Prof. Fedora Jelezka and Dr. Genka Genova from Ulm University and Prof. Jianming Cai of Huazhong University of Science and Technology. They introduced an innovative strategy that exploits the cross-correlation between two noise sources.
By exploiting the destructive interference of cross-correlated noise, the team was able to significantly extend the coherence time of quantum states, improve control fidelity, and increase sensitivity for high-frequency quantum sensing.
Schematic representation of destructive cross-correlated noise interference, control sequence and experimental setup. Credit: Physical inspection letters (2024). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.132.223601
The main achievements of this new strategy include:
- Tenfold increase in coherence time: The time that quantum information remains intact is extended ten times longer compared to previous methods.
- Improved Control Fidelity: Increased precision when manipulating quantum systems leads to more precise and reliable operations.
- Superior sensitivity: The ability to detect high-frequency signals surpasses the state of the art and enables new applications in quantum sensing.
Salhov said: “Our innovative approach expands our toolkit for protecting quantum systems from noise. By focusing on the interplay between multiple noise sources, we have unlocked unprecedented levels of performance, bringing us closer to the practical implementation of quantum technologies.”
This advance not only marks a significant leap in the field of quantum research, but also holds promise for a wide range of applications. Industries that rely on highly sensitive measurements, such as healthcare, will benefit enormously from these improvements.
More information:
Alon Salhov et al, Protecting quantum information through destructive interference of correlated noise, Physical Review Letters (2024). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.132.223601
Provided by the Hebrew University of Jerusalem
Citation: New method achieves tenfold extension of quantum coherence time through destructive interference of correlated noise (2024, 10 July) Retrieved 11 July 2024 from https://phys.org/news/2024-07-method-tenfold-quantum-coherence-destructive .html
This document is subject to copyright. Except for any bona fide act for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content is provided for informational purposes only.